Get notified of page updates
Melanoma: Screening and Early Detection
Learn about expert guidelines for melanoma screening. Stay up to date by signing up for our community newsletter.
Explore More Pages via Quick Links
Overview
Melanoma: Screening and Early Detection
Melanoma: Risk Reduction
Glossary on
off
Screening for Melanoma
The following types of screening may be recommended for people at high risk for melanoma:
- Skin self exams involve a person checking their own skin on a monthly basis to look for changes or abnormalities. Experts recommend training high risk people to perform exams.
- Watch moles closely for any signs of change in shape, size, or color.
- Dermatologists may take pictures of the skin and moles, known as mole mapping, or full body photography.
- Dermatologists examination of moles with a hand-held device known as a dermatoscope.
- Ophthalmologic examinations to check for melanoma in the eye.
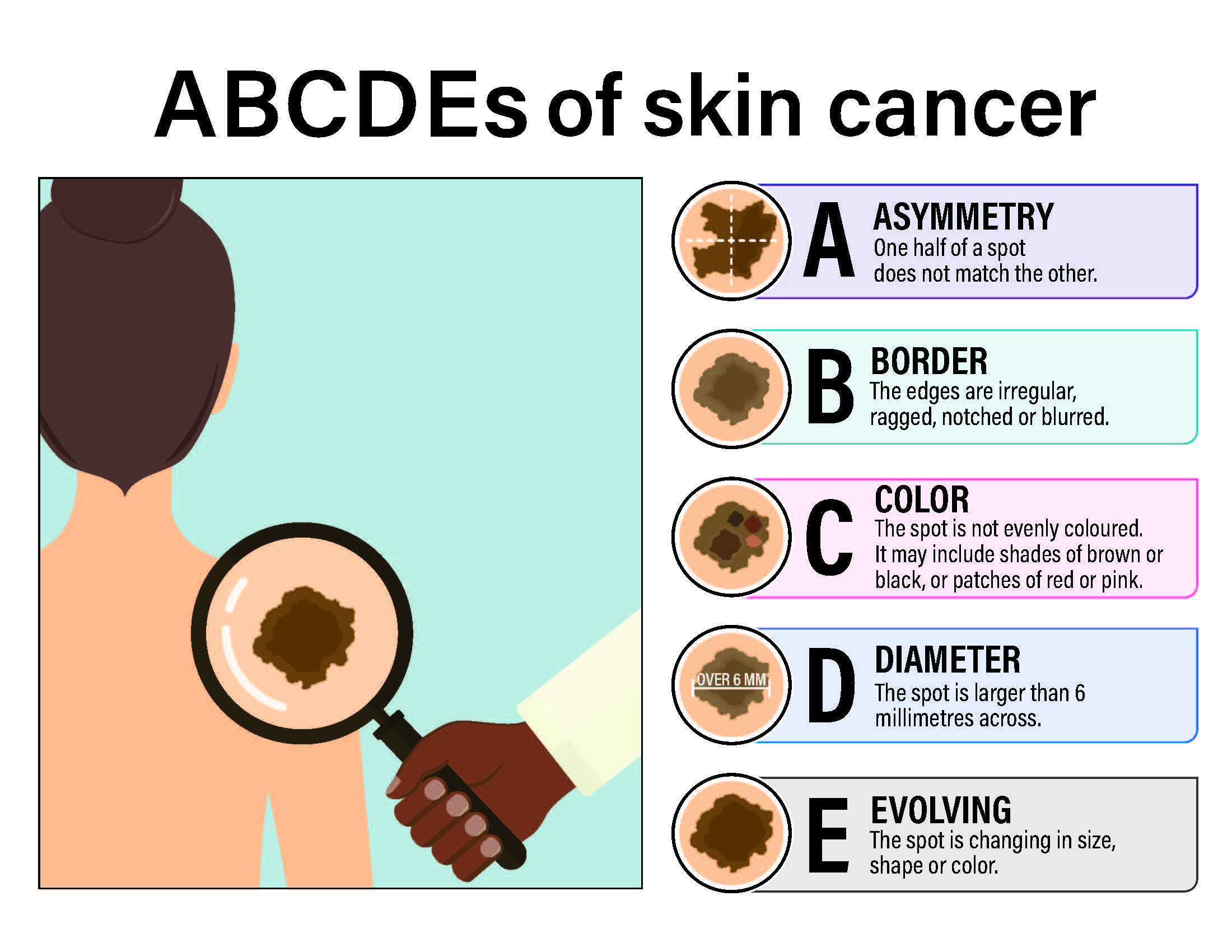
What are the signs of melanoma?
One way to remember the signs of melanoma are to pay attention to and report to your doctor any moles that follow the ABCDE rule:
- Asymmetry
- Borders that are irregular
- multiple Colors
- Diameter of over 6 millimeter
- Evolving or changing in size, shape or color
Screening for high-risk people
Gene |
Recommendation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Source: Lalloo, F., Kulkarni, A., Chau, C. et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and surveillance of BAP1 tumour predisposition syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 31, 1261–1269 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-023-01448-z; Source: NCCN Guidelines: Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Breast, Ovarian, Pancreatic, vs. 2 2025. |
|
More Resources

Find a Dermatologist
The American Academy of Dermatology has a tool to find dermatologists by expertise, location or procedure.
NCCN Patient Guidelines for Melanoma
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network has patient guidelines to help people diagnosed with melanoma make informed decisions.
AIM at Melanoma Foundation
FORCE partner, AIM at Melanoma Foundation has detailed information to help people understand their diagnosis and treatment options.
Last updated November 07, 2024